182
Se puede resumir que el receptor con diabetes tipo 2 debe
cumplir las siguientes características: edad menor a 60 años,
IMC
<
30kg/m
2
, nivel péptido C
<
10ng/ml, dosis de insulina
diaria mayor a 1U/kg/día, uso de insulina por más de 5 años,
historia de adherencia a tratamientos, dieta satisfactoria,
ausencia de amputaciones, tabaquismo, y enfermedad
cardiovascular severa (7).
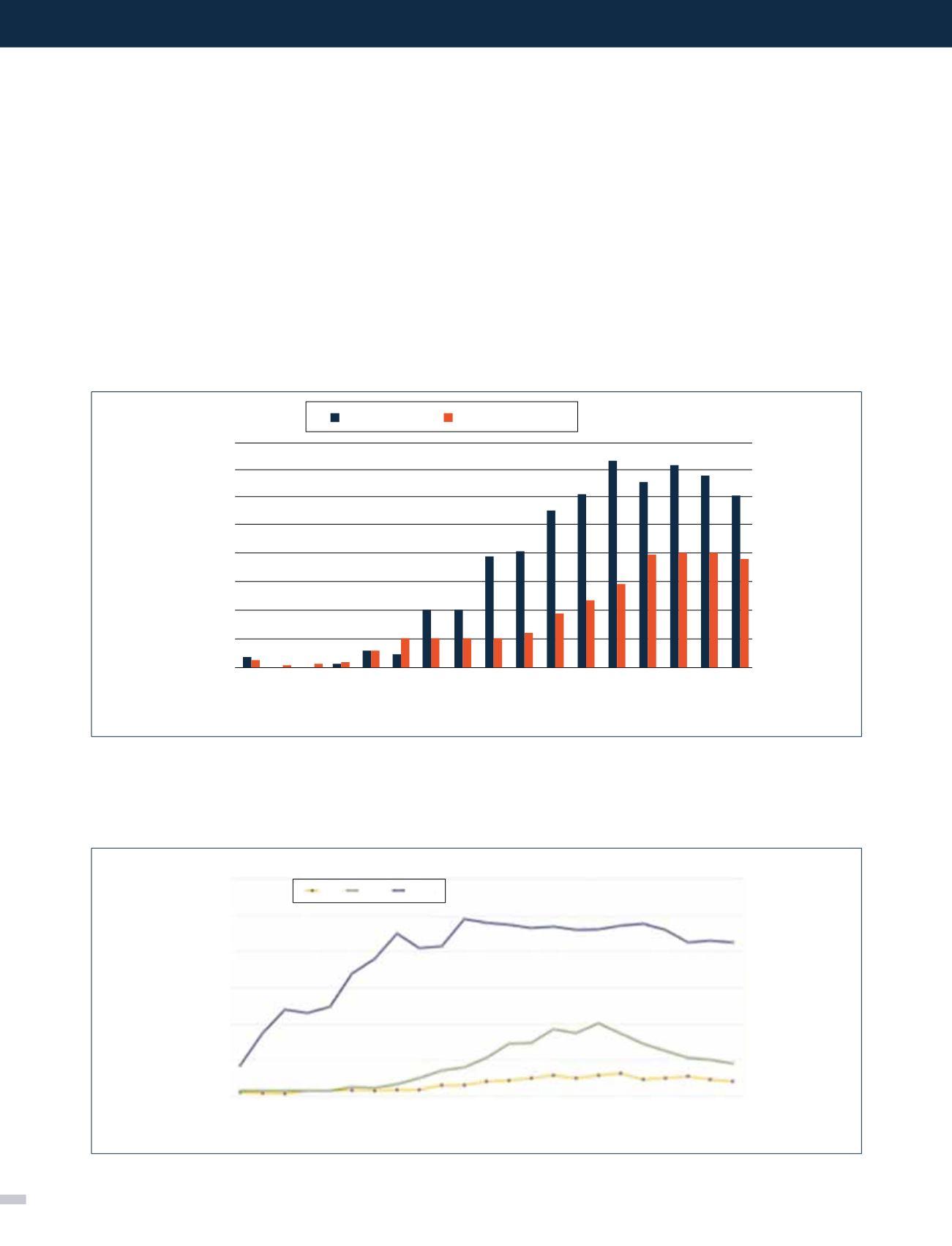
Figura 1. NÚMERO ANUAL DE TRASPLANTE DE PÁNCREAS EN ESTADOS UNIDOS PERIODO 1966-2010
Figura 2. NÚMERO ANUAL DE TRASPLANTE DE PÁNCREAS SOLITARIO (TPS).TRASPLANTE PANCREÁTICO DESPUÉS
DE TRASPLANTE RENAL (TPTR), TRASPLANTE SIMULTÁNEO PÁNCREAS RIÑÓN (TSPR) EN ESTADOS UNIDOS PERIODO
1988-2010
Realidad actual del trasplante de páncreas en
Chile y en el mundo
Como muestra la Figura 1, el trasplante pancreático se ha
desarrollado como una real alternativa terapéutica en los
últimos 20 años. Este trasplante actualmente se puede realizar
en tres modalidades, el más frecuente es el trasplante riñón-
páncreas simultáneo, seguidos por el trasplante de páncreas
aislado y trasplante de páncreas después del trasplante de
riñón (Figura 1 y 2) (1).
[REV. MED. CLIN. CONDES - 2016; 27(2) 179-187]
Trasplante de Páncreas (n)
Trasplantes (n)
US: n=25030
Non US: n=12,075
Pre 78
1988 1990 1992 1994 1996 1998 2000 2002 2004 2006 2008 2010
1979 1981 1983 1985 1987 1989 1991 1993 1995 1997 1999 2001 2003 2005 2007 2009
1600
1400
1200
1000
800
600
400
200
0
Año
Año
1200
1000
800
600
400
200
0
TPS TPTR TSPR








